What is a Microcontroller?
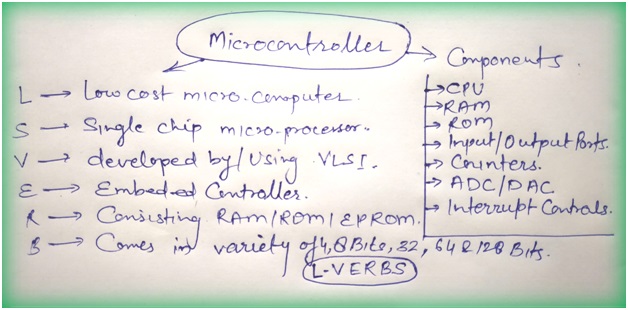
- A microcontroller is a single-chip microprocessor that is manufactured using VLSI technology.
- Because the microcontroller and its supporting circuitry are frequently incorporated into or embedded in the devices they control, a microcontroller is also known as an embedded controller.
- On the other hand we can say...(A microcontroller is a compact, low-cost microcomputer designed to do certain embedded system activities such as displaying microwave information, receiving distant signals, and so on.)
- The CPU, memory (RAM, ROM, EPROM), serial ports, peripherals (timers, counters), and other components make up a generic microcontroller.
- Microcontrollers, like microprocessors, come in a variety of word lengths (4bit,8bit,16bit,32bit,64bit and 128-bit microcontrollers are available today).
 |
| Microcontroller Chip |
A microcontroller is made up of one or more of the following components:
- Central processing unit(CPU).
- Random Access Memory)(RAM).
- Read Only Memory(ROM).
- Input/output ports.
- Timers and Counters.
- Interrupt Controls.
- Analog to digital converters.
- Digital analog converters.
- Serial interfacing ports.
- Oscillatory circuits.
- Internally, a microcontroller contains all of the capabilities necessary for a computing system, and it works as a computer without the addition of any external digital components.
- The user may program the majority of the pins on the microcontroller chip.
- A microcontroller has a lot of bit handling instructions that the programmer can understand.
- Boolean functions can be handled by a microcontroller.
- Increased speed and efficiency.
- A microcontroller's on-chip ROM structure improves firmware security.
- Designing is simple and inexpensive, with a minimal footprint.
Microcontroller structure
- A microcontroller's brain is the CPU. The CPU is in charge of fetching the instruction, decoding it, and then executing it.
- The CPU combines all of the components of a microcontroller into a single system. The CPU's main job is to fetch and decode instructions.
- The CPU must decode the instruction retrieved from program memory.
Random Access Memory)(RAM).
- Memory in a microcontroller serves the same purpose as memory in a microprocessor. It's where you keep your data and programs.
- For storing program source codes, microcontrollers often have a set quantity of RAM and ROM (EEPROM, EPROM, etc.) or flash memories.
Input/output ports (Parallel input/output ports).
- Parallel input/output ports are mostly used to drive/interface various devices to a microcontroller, such as LCDs, LEDs, printers, memory, and so on.
- Serial ports connect a microcontroller to other peripherals such as parallel ports and provide numerous serial interfaces.
Timers and Counters.
- This is one of the microcontroller's most helpful functions. There may be multiple timers and counters on a microcontroller.
- Inside the microcontroller, timers and counters provide all timing and counting functions.
- This portion performs clock functions, modulations, pulse creation, frequency measurement, and oscillations, among other things.
- This can be used to count external pulses as well.
Analog to digital converters.
- The analogue signal is converted to digital form using ADC converters.
- The input signal to this converter should be analogue (for example, sensor output), and the output should be digital.
- The digital output can be used for a variety of digital tasks (e.g. measurement devices).
Digital to Analog Converter (DAC).
- The DAC reverses the ADC conversion process. The digital signal is converted into analogue format by the DAC.
- It is commonly used to control analogue devices such as DC motors, different drives, and so on.
Serial interfacing ports.
- The interrupt control is used to provide a functional program with an interrupt (delay).
- The interrupt can be external (initiated by using the interrupt pin) or internal (triggered by using the interrupt pin) (by using interrupt instruction during programming).
Oscillatory circuits.
- Some microcontrollers are exclusively utilized for a few specific applications (for example, space systems and robotics), and these controllers have extra ports to accomplish these activities.
- This is regarded as a unique functional block.